
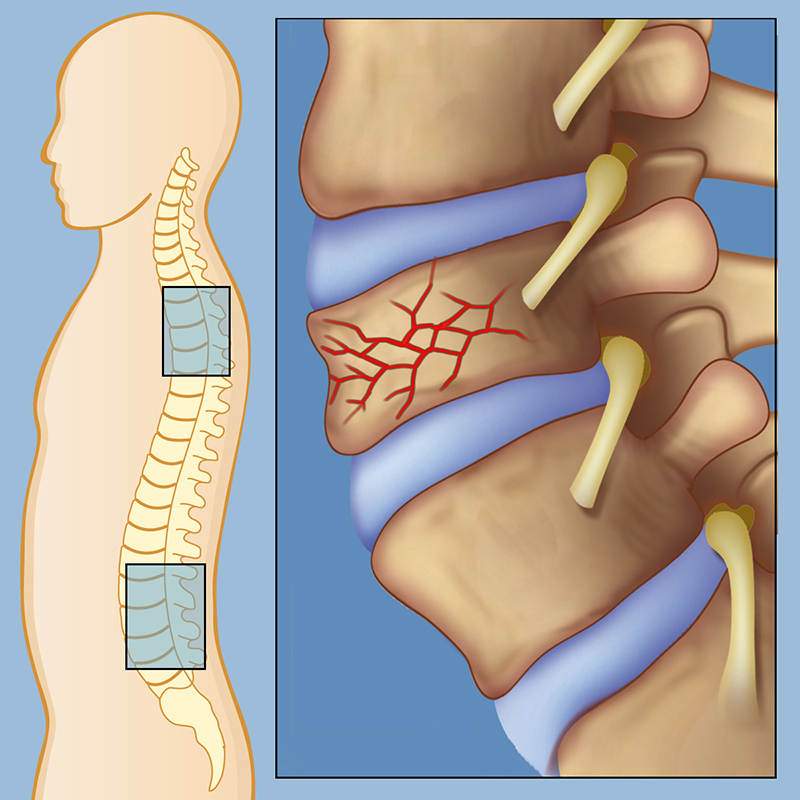
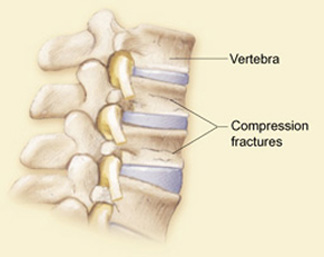
This mostly happens to the front of the vertebrae, making you stoop over time. Your vertebrae (spinal bones) may collapse, becoming shorter overall. What happens if I have compression spinal fractures? The age of the fracture is sometimes important to know to help guide treatment options.A compression spinal fracture is when a bone in your spine becomes compressed or collapsed.
An MRI can also tell if the fracture is old or new.Ī nuclear bone scan - May be used to help determine when the fracture occurred. Based on the patient's history and physical exam, if a vertebral fracture is suspected, an X-ray will be ordered to confirm the diagnosis.ĭepending on the physician's findings from the patient's history, physical exam and X-ray, additional diagnostic tests may also be needed, such as:Ī CT scan - To see whether the fractured bone is stable and if nerves near the fracture are being irritated or affected by the fracture.Īn MRI - May be ordered if the doctor suspects another cause of the patient’s pain, or if there is a chance that nerves near the fracture are affected. If a vertebral compression fracture is suspected, the doctor will test for tenderness and sensitivity near specific vertebrae along the spine. The diagnostic process includes a complete history of the patient's condition, medical history and family history.Īfter taking the patient's history, the physician will do a physical examination in an effort to determine the cause of the pain and rule out other possible problems.

Cancer or multiple myeloma should be considered in patients who also have hypercalcemia, otherwise unexplained anemia, weight loss or proteinuria. It is not uncommon for metastatic cancer that starts in another part of the body to spread to bones in the spine.Ī compression fracture of the spine that appears for little or no reason may be the first indication that an unrecognized cancer has spread to the spine. Tumors also can weaken the spinal vertebrae to the point where they may fracture. Such trauma could come from a fall, a forceful jump, a car accident or any event that stresses the bones in the spine past its breaking point. Trauma to the spinal vertebrae also can lead to minor or severe fractures.
Spinal fractures due to osteoporosis often occur while a person is doing something that causes relatively minor trauma to the spine, such as opening a window, suffering an insignificant fall or twisting while lifting.Īdvanced cases of osteoporosis can lead to a vertebral fracture being caused by routine activities that normally would not cause trauma, such as sneezing, coughing or turning over in bed. These compression fractures can cause a great deal of pain and can permanently alter the shape and strength of the spine. The thinning bones can collapse during normal activity, leading to a spinal fracture. Osteoporosis causes bones to thin and become brittle and weak. It is more common than most people think in people between the ages of 40 and 50, and it is reasonably common in men over age 50. Osteoporosis is by far the most common cause of vertebral compression fractures, especially in women over age 50. As a result, about two-thirds of the vertebral fractures that occur each year are not diagnosed and therefore are not treated. Instead, the patient's pain is often just thought of as general back pain - such as from a muscle strain or other soft-tissue injury - or as a common part of aging. Less intense pain while lying on one's backīecause the majority of damage is limited to the front of the vertebral column, the fracture is usually stable and rarely associated with any nerve or spinal cord damage.Ī common problem with a vertebral fracture is that it is not recognized or accurately diagnosed.The main clinical symptoms of vertebral fractures typically include one or a combination of the following: Vertebral fractures are usually followed by acute back pain and may lead to chronic pain, deformity (thoracic kyphosis, commonly referred to as a dowager's hump), loss of height, crowding of internal organs, and loss of muscle and aerobic conditioning due to lack of activity and exercise.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
